Reflection Detection of GNSS RO Measurements
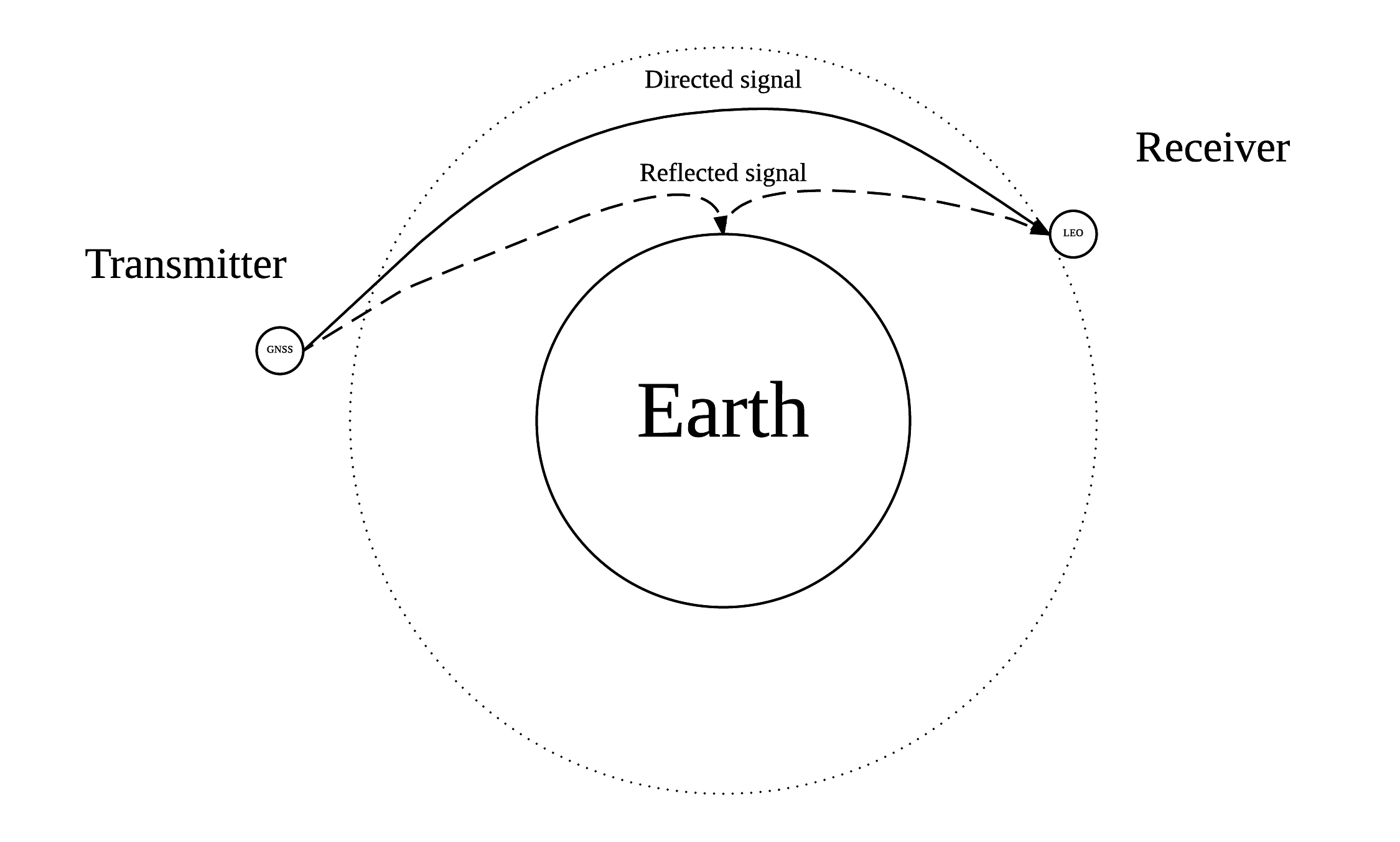
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) radio occultation (RO) has been widely used in the prediction of weather, climate, and space weather, particularly in the area of tropospheric analyses. However, one of the issues with GNSS RO measurements is that they are interfered with by the signals reflected from the earth’s surface. Many GNSS RO events are subject to such interfered GNSS measurements, which are considerably difficult to extract from the GNSS RO measurements.
To precisely identify interfered RO events, an improved machine learning approach-an artificial neural network (ANN)-aided radio-holography method is proposed in this paper. This approach was validated using Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate/FC-3 atmPhs (level 1b) data during the period of day of year 172-202, 2015, and its detection results were compared with the flag data set provided by Radio Occultation Meteorology Satellite Application Facilities for the performance assessment and validation of the new approach.
Holographic Metrics
where and
are the SNR (which is regarded as the amplitude) and phase of the signal respectively at epoch t, and 𝑖 is the symbol for imaginaries.
obtained by the one-dimensional second-order function best fitted to the raw excess phase. Then
is decomposed from the time domain to the frequency domain by the Multiple Signal Classification (MUSIC) algorithm for producing radio holographic matrices.
Detailed Procedures
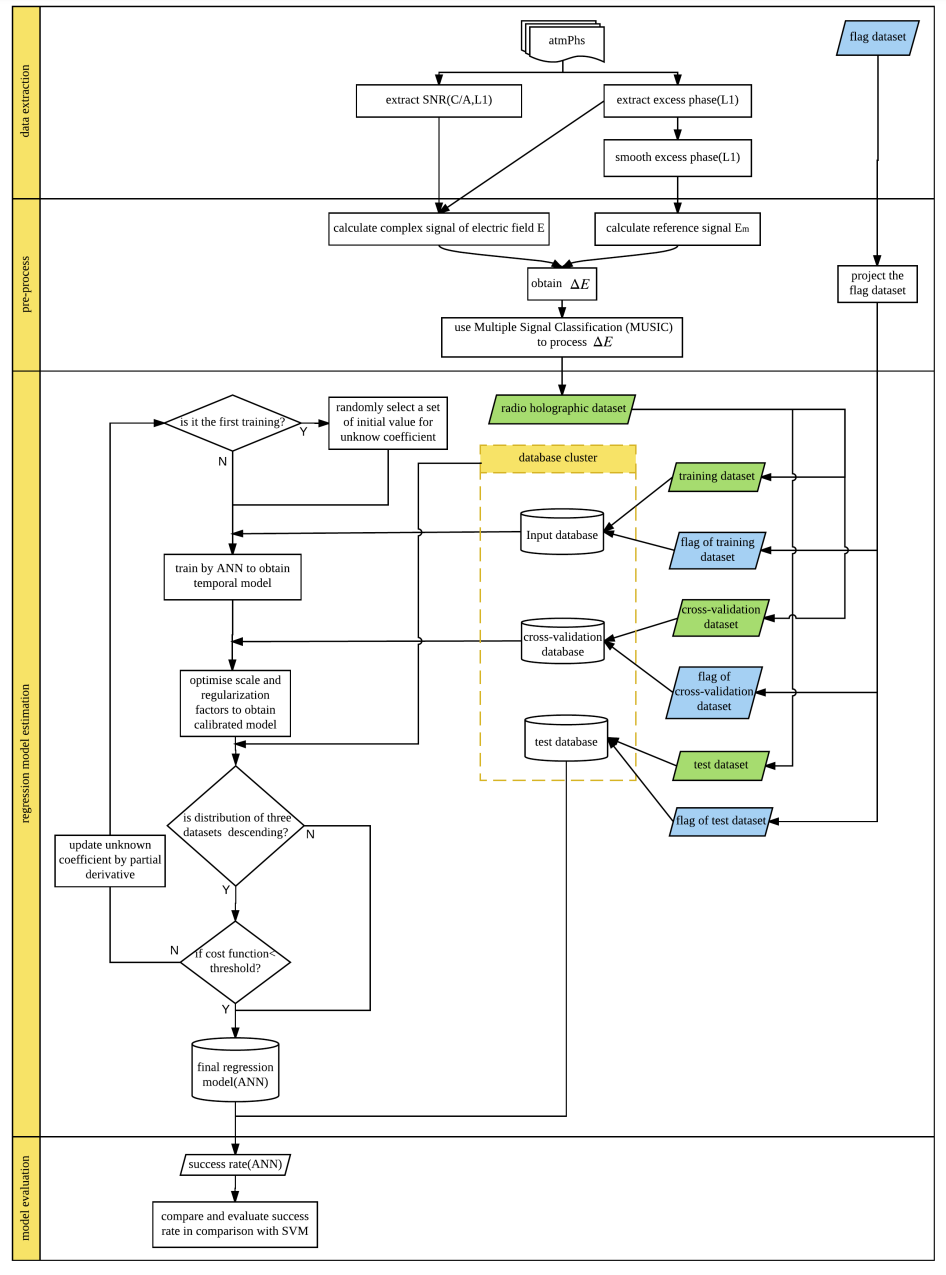
Fig. Flowchart of the new methodology
Results
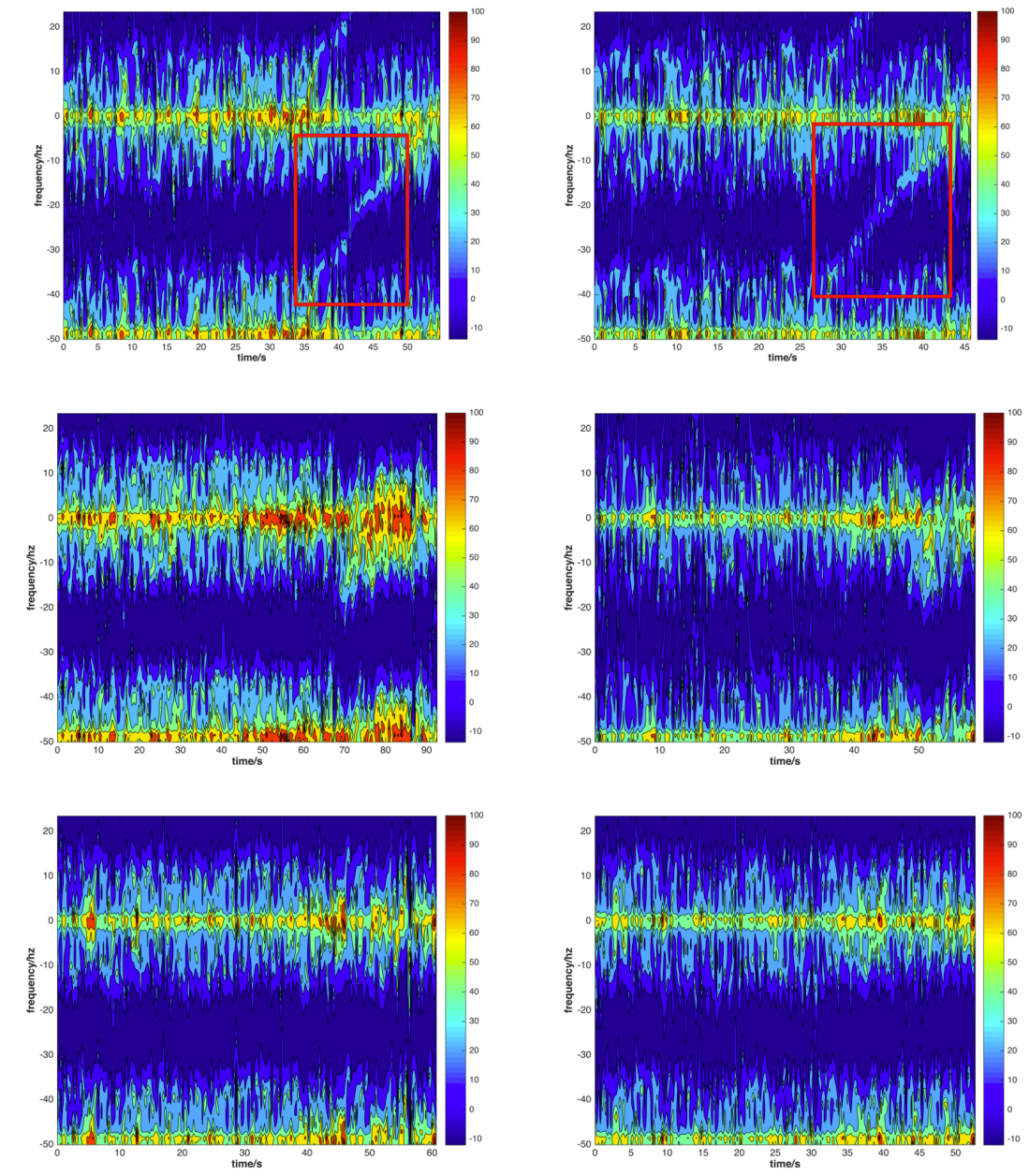
Fig. Radio-holographic figures for three cases − clear reflection (top), unclear reflection (middle) and clear noreflection (bottom), the X- and Y-axis are time and frequency respectively. It is noted that the content of radio hologram in the frequency band -50 to -25 Hz equals to those between 0 to 25 Hz.
